Mechanical Engineering Program Framework
Programme Educational Objectives (PEOs) & Learning Outcomes (PLOs)
1. Programme Educational Objectives (PEOs)
PEO1: Advanced Technical Expertise in ME
To produce **mechanical engineers** with advanced technical expertise capable of addressing complex **mechanical systems design and analysis** problems in professional practice and research, on a national and international level. (Aligned with ITC Mission #1 and #2: talented and skilled engineers)
PEO2: Lifelong Learning & Social Responsibility
To cultivate lifelong learners who embody integrity and responsibility in their roles within industry, society, and the environment, ensuring ME solutions ethically address **safety standards and sustainability goals**. (Aligned with ITC Mission #1: cultivate lifelong learners)
PEO3: Entrepreneurial Spirit & Innovation
To produce entrepreneurial spirit by fostering innovation in **mechanical product development and advanced manufacturing processes**, supporting the creation of start-ups and new technologies. (Aligned with ITC Mission #2: entrepreneurial spirit)
PEO4: Technology & Digital Tools
To foster **mechanical engineers'** ability to leverage advanced technology and digital tools, such as **CAD, FEA, and simulation software**, to unlock new efficiencies, capabilities, and design opportunities. (Aligned with ITC #2:Technology & digital tools)
2. Programme Learning Outcomes (PLOs)
Click on a Domain to view the detailed Learning Outcomes.
PLO1: Explain theories, concepts, and procedures that support core **Mechanical Engineering** areas (e.g., thermodynamics, solid mechanics, and fluid dynamics). (~C2)
PLO2: Upon completion of the program, students can investigate, model, and critically analyze complex design and thermal problems in **Mechanical Engineering**. (~C4)
PLO3: Graduates will operate laboratory and workshop equipment accurately and safely, including basic **measuring and manufacturing tools**. (~P3)
PLO4: Contribute to and facilitate constructive resolution of issues in group situations, whether in a leadership role or as a team member. (~A4)
PLO5: Organize and prioritize responsibilities to demonstrate commitment and accountability for assigned design and project tasks. (~A4)
PLO6: Integrate attention to detail and task-related values systematically to ensure thoroughness and reliability in work and design outcomes (Entrepreneurial skills). (~A4)
PLO7: Follow safety and housekeeping procedures consistently and demonstrate ethical professional conduct to maintain a safe working environment (Ethics and Professionalism). (~A4)
PLO8 – Digital skills: By the end of the program, students will use specialized **ME digital tools (e.g., CAD, simulation)** competently and independently. (~P4)
PLO9 – Numerical Skills: By the end of the program, students will be able to analyze complex problems based on **numerical, statistical, and experimental data**. (~C4)
PLO10 – Communication: Students will communicate complex technical information effectively both orally and in writing. (~P4)
3. PLO to PEO Mapping
The table below illustrates the sample mapping between the Programme Learning Outcomes (PLOs) and the Programme Educational Objectives (PEOs). **Click any row to highlight its connections.**
| PLO | PEO 1 (Technical ME) |
PEO 2 (Social/Learn) |
PEO 3 (Entrepreneurial) |
PEO 4 (Digital Tools) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLO 1 | ✓ | |||
| PLO 2 | ✓ | |||
| PLO 3 | ✓ | |||
| PLO 4 | ✓ | |||
| PLO 5 | ✓ | |||
| PLO 6 | ✓ | |||
| PLO 7 | ✓ | |||
| PLO 8 | ✓ | |||
| PLO 9 | ✓ | |||
| PLO 10 | ✓ | |||
| Total | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Mechanical Engineering 2025
The Mechanical Engineering degree program is designed to lay a solid foundation in designing, analyzing, and producing mechanical systems and equipment. The curriculum is enhanced with state-of-the-art technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), equipping graduates to address complex challenges in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. The program offers hands-on laboratory experiences, interdisciplinary coursework, and opportunities for research, ensuring a well-rounded education. The program upholds high academic and professional standards, fostering professionalism and a strong work ethic. Students are prepared for dynamic careers in design, manufacturing, robotics, and energy sectors, supported by robust career services and networking opportunities.
Program Goals
Our goal is to educate versatile mechanical engineers prepared to excel across diverse industries. Students will develop advanced skills in emerging digital technologies, driving innovation in design, manufacturing, robotics, building systems, and the energy sector. Our program combines hands-on labs, interdisciplinary coursework, and foundational engineering principles to prepare graduates for dynamic careers. We emphasize professionalism and ethical practices, aiming to produce engineering leaders who are highly valued in the global job market.
Course lists
Subjects for General Education in Foundation Years (Year 1&2):
- Geometry
- Mechanics
- Management and Accounting
- Philosophy
- Environment
- Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Probability
- Thermodynamics
- Technical Drawing
- Market
- Information Technology
- History
- Chemistry
- Electricity
- French
- English
Subjects for year 3
- French
- English
- Statistics
- Mechanics
- Computer Aid Design (CAD)
- Materials Sciences I
- Introduction to Control Theory
- Fluid Mechanics and Transfer Process
- Mechanical Design
- Introduction to AI for Engineering Applications
- Strength of Materials
- Electricity and Electronics
- Introduction to Manufacturing Engieering
- Metal Machining, Metrology
Subjects for year 4
- French
- English
- Internship Report
- Industrial Hydraulics
- Electronics
- Machine Element
- Statically Indetermine Structure
- Dynamics of Gas
- Applied Thermodynamics
- Mechanical Construction
- Internal Combustion Engines
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning I
- Turbomachines
- Heat Exchangers
- Numerical Method for Engieering
- Finite Element
Subjects for year 5
- Professional Integration
- English for Work and Carrer Engineering Skills
- Research Methodology
- Theory of Engines
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning II
- Thermics of Locals
- Referigeration and Air Conditioning Project
- Enterprises Organization and Management
- New and Renewable Energies
- Vibration
- Power Plant Engineering
- Final Year Internship and Thesis Defense
Career path
Graduated students from Mechanical Engineering have diverse carrer opportunities across multiple sections including:
1. Design and Site Engineering: specialize as Design or Site Engineers, focusing on the installation and maintenance of HVAC systems in various types of buildings, including residential, commercial, medical, and industrial facilities.
2. Manufacturing: In manufacturing plants, mechanical and industrial engineers are pivotal in production, quality assurance, product design, machinery maintenance, management, and energy management.
3. Automation and Robotics: There is increasing demand for engineers in the automation and robotics fields, where they design, implement, and maintain automated systems.
4. Sustainability and Green Technologies: Engineers are also at the forefront of developing sustainable technologies, working on renewable energy systems and materials recycling to enhance environmental conservation.5. Supply Chain Management: These engineers optimize supply chains, improving logistics, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency in production and distribution networks.
6. Project Management: Mechanical and industrial engineers often assume project management roles, overseeing projects from start to finish, ensuring they adhere to deadlines, budgets, and quality standards.
7. Technical Consulting and Energy Auditing: Engineers can become Technical Consultants and Energy Auditors, assessing systems and recommending improvements for better efficiency.
8. Academic and Research Roles: Opportunities extend to academia and research, where engineers can contribute as technical trainers and researchers.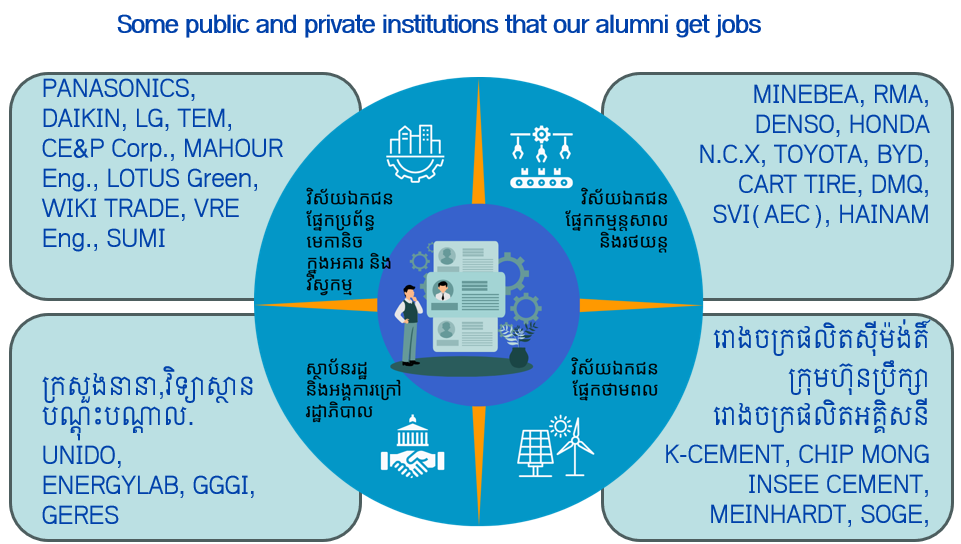
Scholarship Opportunity
After graduation, students also have opportunity to pursue their Master and PhD degree from universities in:
- France
- Belgium
- Japan
- South Korea
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Malaysia
- China
- Other countries ( Asia, EU, …)

